Glass Cutting
Our Swiss Bystronic cutting line is fully automated with the ability to delete the edges of soft coating high performance glass products necessary for correct bonding of edge sealants.
We have a range of glass include from 4mm up to 19mm and a variety of high performance solar control and Low-E
glass.
The fully automated glass cutting system is able to storing Jumbo size sheets 6000x3210mm to allow the best optimization by using the largest stock sizes.
Edge deletion could be made on the cutting table to an increased depth to allow the fritted border to be applied which protects the edge sealant for UV and provides a better aesthetic for structural products.
Tempered Glass
Toughened or tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared with normal glass. Tempering creates balanced internal stresses which cause the glass, when broken, to crumble into small granular chunks instead of splintering into jagged shards. The granular chunks are less likely to cause injury.
Furnace information
North glass
Heat mode top convection
Heat source electric
Lowest emissivity 0.03
Flat tempered glass 4 mm : 19 mm
4mm glass largest size 220 cm : 240 cm
5mm: 19mm largest size 240 cm: 500 cm
Curved tempered glass 6mm : 12mm minimum radius 100 cm/ Maximum radius 500 cm
Advantages:
The term toughened glass is generally used to describe fully tempered glass but is sometimes used to describe heat strengthened glass as both types undergo a thermal ‘toughening’ process.
There are two main types of heat treated glass: heat strengthened and fully tempered. Heat strengthened glass is twice as strong as annealed glass while fully tempered glass is typically four to six times the strength of annealed glass and withstands heating in microwave ovens. The difference is the residual stress in the edge and glass surface. Fully tempered glass in the US is generally rated above 65 MPa (9427 psi) in pressure-resistance while heat strengthened glass is between 40 and 55 mega pascals (5801 and 7977 psi respectively).
It is important to note that the tempering process does not change the stiffness of the glass. Annealed glass deflects the same amount as tempered glass under the same load, all else being equal. But tempered glass will take a larger load, and therefore deflect further at break.
Applications:
Toughened glass is used when strength, thermal resistance and safety are important considerations. It is used in a wide range of applications including:
External Glazing: Curtain walls Structural Glazing Spider Fitting
Architectural Shower Cubicles:
Partitions.
Handrails & Balustrades.
Glass Doors & Windows.
Commercial/Residential Fixed and Operable Windows Displays.
Curved Tempered Glass
Curved tempered is a type of glass that is heat treated and bent or curved to create a unique profile for installations in commercial and residential applications. It is tempered by heat treating glass through a horizontal tempering furnace.
Curved tempered glass is available for insulated glass units using clear, tinted, reflective and Low-E glass(including new generation of post-temperable Low-E coatings)
Fabrication Options Holes, notches, hinge cutouts; polished, ground and mitered edges; pattern cuts.
Guidelines for hole sizes and positioning must be considered during the design phase, and fabrication processes must be completed before heat treatment. Fabrication can be done with any thickness of glass intended in use for a curved glass application.
With this capability, curved tempered glass is ideal for unique and elegant shower enclosures.
Glass options curved tempered glass is offered in a large variety of glass types to achieve the desired aesthetics and to meet design criteria.
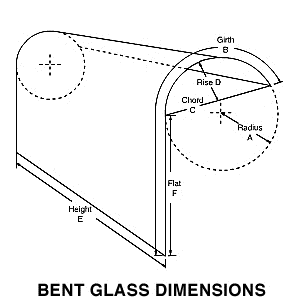
Applications:
Typical applications include glass Curtain Walls, Handrail Shower enclosures, revolving doors, partitions and insulated glass units.
Depending on different designs, there is specific information that will be required to ensure accuracy.
Capabilities:
Curved tempered glass is available from 6mm-19mm thicknesses
Maximum radius 500 cm. minimum radius 100 cm

Insulated glazing
Also known as double glazing (as most people call it) are double or triple glass window panes separated by an air or other gas filled space to reduce heat transfer across a part of the building envelope.
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) are manufactured with glass in range of thickness from 3 mm to 10 mm or more in special applications. Laminated or tempered glass may also be used as part of the construction. Most units are manufactured with the same thickness of glass used on both panes but special applications such as acoustic
attenuation or security may require wide ranges of thicknesses to be incorporated in the same unit.
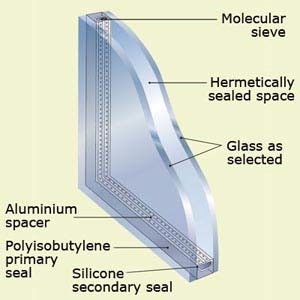
A sample unit of a DG system is shown through the side figure.
Applications:
Typical applications include glass Curtain Walls, Handrail Shower enclosures, revolving doors, partitions and insulated glass units.
Depending on different designs, there is specific information that will be required to ensure accuracy.
Advantages of insulated glass:
Thermal Insulation:
The maximum insulating efficiency of a standard IGU is determined by the thickness of the space containing the gas. Typically, most sealed units achieve maximum insulating values using a gas space of 16–19 mm (0.63–0.75 in) when measured at the center of the IGU. When combined with the thickness of the glass panes being used, this can result in an overall thickness of the IGU of 22–25 mm (0.87–0.98 in) for 3 mm (0.12 in) glass to 28–31 mm (1.1–1.2 in) for 6.35 mm (0.250 in) plate glass.
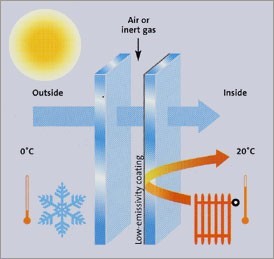
The Figure shows the thermal insulation advantage in the use of a Low-E coating glass
Applications:
We can use insulated glazing units in:
Windows& Doors (either Aluminum or U-PVC)
Facades (Curtain walls, Structural and Semi-Structural Glazing)
Laminated Glass
Or has known by safety glass is a type of glass that holds together when shattered. In the event of breaking, it is held in place by an interlayer, typically of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), between its two or more layers of glass. The interlayer keeps the layers of glass bonded even when broken, and its high strength prevents the glass from breaking up into large sharp pieces. This produces a characteristic “spider web” cracking pattern when the impact is not enough to completely pierce the glass.
A typical laminated makeup would be 3mm glass / 0.38 mm interlayer / 3mm glass. This gives a final product that would be referred to as 6.38 mm laminated glass.
Multiple laminates and thicker glass increases the strength. Bullet-resistant glass is usually constructed using polycarbonate, thermoplastic, and layers of laminated glass. A similar glass is often used in airliners on the front
windows, often three sheets of 6mm toughened glass with thick PVB between them.
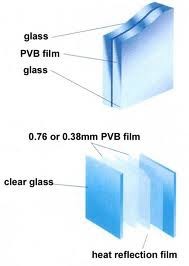 The figure shows the laminated glass components
The figure shows the laminated glass components
Since 2004 metallized and electro conductive PET-Interlayers are used as substrate for light emitting diodes and laminated to or between glass.
- Top Layer: Glass
- Interlayer: Transparent thermoplastic material e.g.: PVB
- Interlayer: LED (light emitting diodes) on transparent conductive Polymer
- Interlayer: Transparent thermoplastic material, e.g.: PVB
- Bottom layer: Glass
Laminated glass is also sometimes used in glass sculptures.
Applications:
Laminated glass is normally used when there is a possibility of human impact or where the glass could fall if shattered, we can use laminated glass in:
Skylight glazing and automobile windshields.
In geographical areas requiring hurricane-resistant construction. Exterior storefronts (curtain walls and windows).
Anti-Bullet Applications: which prevents the vital places like banks, museums and governmental organizations from being penetrated or attacked.

The PVB interlayer also gives the glass a much higher sound isolation rating, due to the damping effect, and also blocks 99% of incoming UV radiation.

